System Architecture
Radica is composed by the following components:
- NFC Tags: ST25TA-E series NFC tags are used to perform authentication of products.
- Mobile Application: A mobile application is used to interact with the NFC tags and the Blockchain to verify the authenticity of products.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are used to store the certificate of authenticity of products on the Blockchain.
NFC Authentication
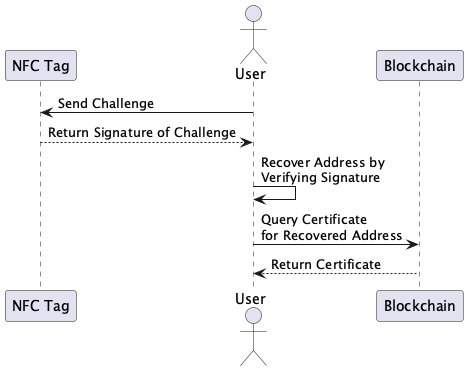
The NFC used can perform on-chip digital signature using the ECDSA algorithm with the secp256k1 curve. This allows to authenticate the chip with an Asymmetric CRA (Challenge Response Authentication) protocol.
Since the algorithm used is the same as the one used in the Blockchain, it is possible to recover a Blockchain address from the signature of the challenge.
Do not send any value and do not assign any permission to the recovered address. An attacker could let the chip sign a forged challenge containing a valid Blockchain transaction.
For the Demo Project, the NFC used is the NTAG215 and not the ST25TA-E. The NTAG215 does not support the ECDSA algorithm, so the authentication is simulated. Refer to Demo
Mobile Application
The mobile application interacts with the NFC tags to perform authentication. A random challenge is generated and sent to the NFC tag to be signed. From the signature it is possible to recover a Blockchain address, you can refer to Public Key Recovery for more info.
The mobile application queries the Radica Smart Contract to verify the authenticity of the product. The smart contract stores the certificate of authenticity of the product.
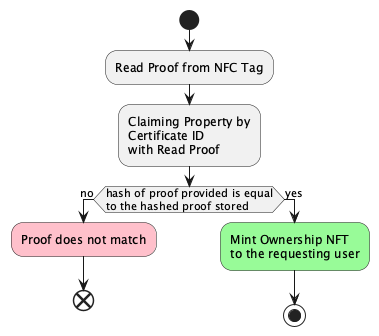
Authentication
The following diagram shows the authentication process:
Claiming Ownership
The user in possess of the product can claim the NFT demonstrating the ownership of the product. The following diagram shows the claiming process: